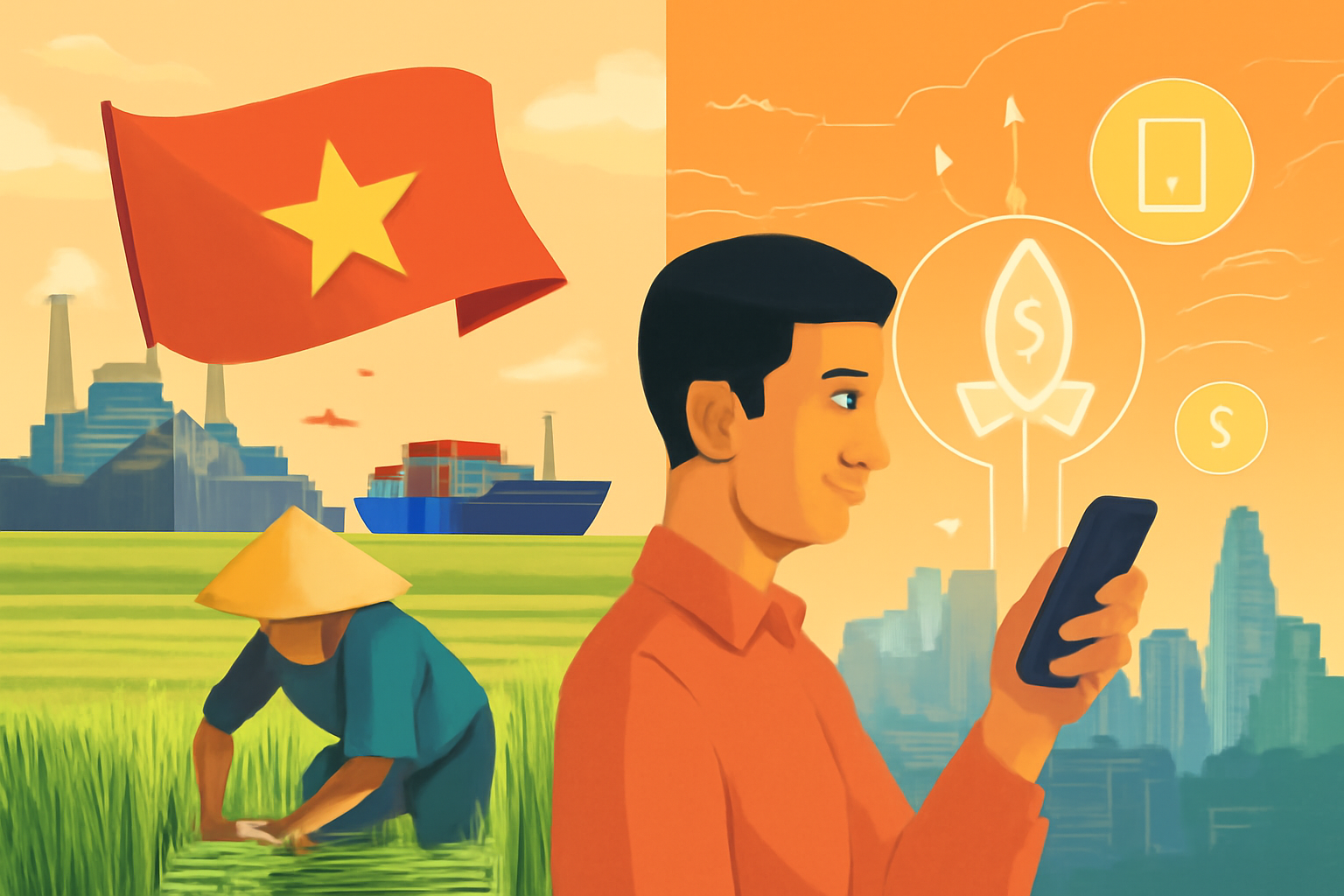
Vietnam’s economic evolution is one of the most remarkable success stories in Southeast Asia. Moving from a primarily agrarian economy to a more diversified industrial and technology-driven economy, Vietnam has established itself as a rising star in the global market. This shift has been shaped by decades of strategic policy decisions and the country’s willingness to engage with global economic trends.
Agriculture: Vietnam’s Economic Starting Point
Vietnam’s economy was traditionally agricultural, with rice as the dominant crop. The country was a major rice exporter, alongside other agricultural products such as coffee, tea, and rubber. For many years, agriculture provided the bulk of employment in Vietnam’s rural areas and supported the economy’s stability.
However, agriculture could not sustain long-term growth on its own. In the 1980s, Vietnam’s leadership realized the need for economic diversification and implemented the “Đổi Mới” reforms. These reforms transitioned the country from a centrally planned economy to a more market-oriented one, opening the door to industrialization and technological development.
Industrial Growth: Strengthening Manufacturing Capabilities
The 1990s saw Vietnam’s rapid industrialization. By attracting foreign investment and establishing export processing zones, the country began to build a strong manufacturing base. The textile, footwear, and electronics sectors, in particular, saw significant growth, transforming Vietnam into a key player in global supply chains.
The electronics industry stands out as one of the most successful stories of Vietnam’s industrial transformation. Major international companies, such as Samsung and Foxconn, set up large production facilities in the country, enabling Vietnam to become a significant exporter of smartphones, televisions, and other consumer electronics.
Technology and Innovation: Vietnam’s Growing Digital Economy
Vietnam has not only modernized its industrial base but also embraced technology as a driver of future economic growth. The government has actively encouraged the development of the digital economy through investments in infrastructure and support for tech startups. The rise of e-commerce, fintech, and software development in Vietnam demonstrates the country’s rapid digitalization.
Companies such as MoMo (a leading digital wallet) and Tiki (an e-commerce platform) have become household names, contributing to the growth of a vibrant digital ecosystem. With a youthful population that is highly adept at using technology, Vietnam has created an environment ripe for innovation in the tech space.
Future Directions: Overcoming Challenges to Sustainable Growth
While Vietnam’s economic transformation is impressive, there are challenges ahead. The country needs to invest in infrastructure and human capital to ensure its continued growth. Furthermore, there are concerns related to environmental sustainability and the potential for rising income inequality as the economy shifts toward high-tech industries.
Nevertheless, Vietnam’s continued focus on industrial and technological development positions it well for future success. The country is on track to become one of the most important economies in Southeast Asia.